Introduction to the TL431
The TL431 is a versatile three-terminal adjustable shunt regulator that is widely used in power supply circuits. It offers a precise reference voltage, excellent temperature stability, and the ability to be configured in a variety of ways to suit different applications. In this comprehensive guide, we will dive into the world of TL431 circuits, exploring their functionality, characteristics, and practical implementations.
Key Features of the TL431
- Adjustable output voltage range: 2.5V to 36V
- Low temperature coefficient: typically 50ppm/°C
- Low output noise
- Excellent long-term stability
- Available in various packages: TO-92, SOT-23, etc.
How the TL431 Works
Basic Structure and Operation
The TL431 consists of a precision voltage reference, an error amplifier, and a control circuit. The device maintains a constant reference voltage between its cathode and reference pin by shunting current from the cathode to the anode. The output voltage can be adjusted by connecting external resistors to set the desired voltage division ratio.
Pinout and Internal Block Diagram
| Pin | Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cathode | Output and feedback pin |
| 2 | Anode | Positive supply and shunt regulation control |
| 3 | Reference | Reference voltage input |
Basic TL431 Circuits
Fixed Output Voltage Regulator
One of the simplest TL431 circuits is a fixed output voltage regulator. By selecting appropriate values for resistors R1 and R2, you can set the desired output voltage according to the following equation:
V_out = V_ref * (1 + R1/R2)
Where V_ref is the internal reference voltage of the TL431, typically 2.5V.
Adjustable Output Voltage Regulator
To create an adjustable output voltage regulator, you can replace the fixed resistor R2 with a potentiometer. This allows you to vary the output voltage within a specific range determined by the potentiometer’s value and the fixed resistor R1.

Advanced TL431 Applications
Over-Voltage Protection (OVP)
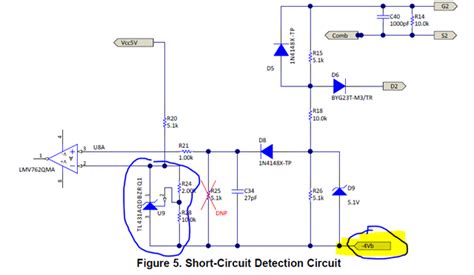
The TL431 can be used to implement over-voltage protection in power supply circuits. By monitoring the output voltage and comparing it with a reference voltage set by the TL431, you can trigger a protection mechanism, such as shutting down the power supply or activating a crowbar circuit, when the output voltage exceeds a predetermined threshold.
Under-Voltage Lockout (UVLO)
Under-voltage lockout is a technique used to prevent a power supply from operating when the input voltage is below a specified level. The TL431 can be configured to provide a precise UVLO threshold by comparing the input voltage with a reference voltage. When the input voltage is insufficient, the TL431 can disable the power supply or provide an indication of the fault condition.
Current Limiting
The TL431 can also be employed in current limiting circuits to protect loads from excessive current. By sensing the current through a shunt resistor and comparing it with a reference voltage, the TL431 can control a pass element, such as a transistor or MOSFET, to limit the current to a safe level.
TL431 Design Considerations
Selecting Resistor Values
When designing TL431 circuits, it is crucial to select appropriate resistor values to ensure proper operation and optimize performance. The key factors to consider include:
- Desired output voltage range
- Maximum cathode current
- Power dissipation in the TL431 and resistors
- Noise and stability requirements
A general guideline is to keep the cathode current within the recommended range specified in the TL431 datasheet, typically between 1mA and 100mA. Higher cathode currents improve regulation accuracy and transient response but increase power dissipation.
Capacitor Selection
Adding a capacitor in parallel with the TL431 can help improve noise performance and stability. The capacitor value should be chosen based on the desired transient response and noise reduction. Typical values range from 0.1μF to 10μF, depending on the application requirements.
PCB Layout Considerations
Proper PCB layout is essential to achieve optimal performance with TL431 circuits. Some key considerations include:
- Minimizing trace lengths to reduce parasitic inductance and resistance
- Providing adequate copper area for power dissipation
- Placing the TL431 and associated components close together to minimize noise pickup
- Using ground planes and proper grounding techniques to reduce noise and improve stability
Troubleshooting TL431 Circuits
Common Issues and Solutions
- Output voltage is incorrect:
- Check resistor values and connections
- Verify the TL431 pinout and orientation
-
Ensure the cathode current is within the recommended range
-
Output voltage is unstable or noisy:
- Add or increase the value of the bypass capacitor
- Check for proper grounding and minimize ground loops
-
Reduce noise pickup by improving PCB layout
-
TL431 overheating:
- Verify that the power dissipation is within the device’s limits
- Increase the cathode resistor value to reduce current
- Improve heat sinking or use a larger package version of the TL431
Measuring and Debugging Techniques
When troubleshooting TL431 circuits, some useful measuring and debugging techniques include:
- Using a multimeter to measure voltages and currents at key points in the circuit
- Monitoring the output voltage with an oscilloscope to check for noise and stability
- Applying a load to the circuit to verify regulation performance
- Using a current probe or shunt resistor to measure current waveforms
- Checking the temperature of the TL431 and other components to ensure they are within safe operating limits
FAQs
-
What is the difference between the TL431 and a fixed voltage reference like the LM336?
The TL431 is an adjustable shunt regulator, which allows you to set the output voltage using external resistors. In contrast, fixed voltage references like the LM336 provide a constant, non-adjustable output voltage. -
Can the TL431 be used as a standalone voltage reference?
Yes, the TL431 can be used as a standalone voltage reference by connecting the cathode and reference pins together and using the anode as the reference output. However, it is more commonly used in conjunction with external resistors to set a specific output voltage. -
What is the maximum output current of the TL431?
The maximum output current of the TL431 depends on the package version and the power dissipation limits. Refer to the device datasheet for specific current ratings. In general, the TL431 is designed for low-current applications, typically up to 100mA. -
How does the TL431 compare to other adjustable voltage regulators like the LM317?
The TL431 is a shunt regulator, which means it regulates the voltage by shunting excess current, while the LM317 is a series pass regulator that regulates the voltage by dropping excess voltage. The TL431 is generally more precise and has better temperature stability, while the LM317 can handle higher output currents. -
Can the TL431 be used in switching power supplies?
Yes, the TL431 is commonly used in switching power supplies for voltage feedback and regulation. It can be used to provide a stable reference voltage for the control circuitry and to monitor and regulate the output voltage through feedback loops.
Conclusion
The TL431 is a highly versatile and precise adjustable shunt regulator that finds applications in a wide range of power supply circuits. By understanding its functionality, characteristics, and various configuration options, you can effectively utilize the TL431 to create stable and efficient voltage regulation solutions. This guide has covered the basics of TL431 circuits, including fixed and adjustable voltage regulators, protection features, and design considerations. With this knowledge, you can confidently incorporate the TL431 into your projects and explore more advanced applications. Remember to refer to the device datasheet for specific parameters and limits, and always prioritize safety and proper design practices when working with power supply circuits.
No responses yet