What is a PreAmp Circuit?
A PreAmp Circuit is an electronic amplifier designed to boost weak audio signals to a higher level before they are fed into the main amplifier or other audio processing devices. The primary goal of a PreAmp Circuit is to increase the signal strength while maintaining a high signal-to-noise ratio and minimizing distortion.
Key Functions of a PreAmp Circuit
-
Signal Amplification: The primary function of a PreAmp Circuit is to amplify the input signal to a level suitable for further processing or amplification.
-
Impedance Matching: PreAmp Circuits help to match the impedance of the source device to the input impedance of the main amplifier, ensuring optimal signal transfer and reducing signal loss.
-
Noise Reduction: By amplifying the signal close to the source, PreAmp Circuits minimize the impact of noise and interference that may be introduced along the signal path.
-
Tone Control: Some PreAmp Circuits include tone control features, allowing users to adjust the bass, midrange, and treble frequencies of the audio signal.
Types of PreAmp Circuits
There are several types of PreAmp Circuits, each designed for specific applications and with unique characteristics:
1. Solid-State PreAmp Circuits
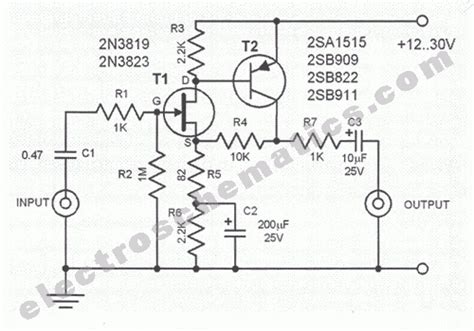
Solid-state PreAmp Circuits use transistors or integrated circuits (ICs) to amplify the input signal. They are known for their reliability, low noise, and compact size. Some popular solid-state PreAmp ICs include:
- NE5532
- OPA2134
- TL072
2. Vacuum Tube PreAmp Circuits
Vacuum tube PreAmp Circuits employ vacuum tubes, also known as valves, to amplify the input signal. They are renowned for their warm, rich, and natural sound, which is often preferred by audiophiles and musicians. Some commonly used vacuum tubes in PreAmp Circuits are:
- 12AX7
- 6922
- ECC83
3. Hybrid PreAmp Circuits
Hybrid PreAmp Circuits combine solid-state and vacuum tube technologies to achieve the best of both worlds. They often use a vacuum tube in the input stage for its desirable sonic characteristics and solid-state components in the output stage for improved reliability and lower output impedance.
Designing a PreAmp Circuit
When designing a PreAmp Circuit, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and sound quality:
1. Gain
The gain of a PreAmp Circuit determines how much the input signal is amplified. The required gain depends on the input source and the desired output level. Typical PreAmp Circuit gains range from 20 dB to 60 dB.
2. Frequency Response
A PreAmp Circuit should have a flat frequency response across the entire audio spectrum (20 Hz to 20 kHz) to maintain the integrity of the input signal. High-quality components and proper circuit design are essential to achieve a linear frequency response.
3. Noise and Distortion
Minimizing noise and distortion is crucial in PreAmp Circuit design. This can be achieved by using low-noise components, proper grounding techniques, and careful circuit layout. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and total harmonic distortion (THD) are important parameters to consider when evaluating a PreAmp Circuit’s performance.
4. Input and Output Impedance
The input impedance of a PreAmp Circuit should be high enough to avoid loading down the source device, while the output impedance should be low enough to drive the next stage efficiently. Proper impedance matching ensures optimal signal transfer and minimizes signal loss.

Applications of PreAmp Circuits
PreAmp Circuits find applications in various audio systems, such as:
-
Home Audio Systems: PreAmp Circuits are used in high-end audio systems to amplify signals from turntables, CD players, or streaming devices before feeding them into power amplifiers.
-
Professional Audio Equipment: Mixing consoles, audio interfaces, and standalone preamps use PreAmp Circuits to amplify signals from microphones and instruments, providing clean and robust signals for recording or live sound reinforcement.
-
Guitar and Bass Amplifiers: PreAmp Circuits are an essential part of guitar and bass amplifiers, shaping the instrument’s tone and providing gain before the signal is sent to the power amplifier stage.
-
Wireless Microphone Systems: PreAmp Circuits are employed in wireless microphone receivers to amplify the low-level signal from the microphone capsule before it is transmitted to the main audio system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between a PreAmp and a power amplifier?
A PreAmp amplifies low-level signals to line-level, while a power amplifier further amplifies the line-level signal to drive speakers or headphones. PreAmps focus on signal quality and gain, while power amplifiers prioritize power output and speaker control.
2. Do I need a separate PreAmp if my audio interface has built-in preamps?
In most cases, the built-in preamps in an audio interface are sufficient for general recording purposes. However, if you require higher-quality preamps with specific features or coloration, a separate PreAmp can be beneficial.
3. Can I use a PreAmp Circuit to improve the sound quality of my phone or laptop?
While a PreAmp Circuit can enhance the sound quality of low-level signals, it may not significantly improve the audio output of devices like phones or laptops, which typically have built-in preamps and digital-to-analog converters (DACs). An external DAC or headphone amplifier may be more effective in enhancing the audio quality of these devices.
4. How do I choose the right PreAmp Circuit for my needs?
When selecting a PreAmp Circuit, consider factors such as the input sources you’ll be using, the desired gain, the required features (e.g., tone controls, phantom power), and compatibility with the rest of your audio system. Research and compare different PreAmp Circuits, read reviews, and, if possible, audition them in person to find the one that best suits your needs and preferences.
5. Can I build my own PreAmp Circuit?
Yes, building your own PreAmp Circuit is possible if you have the necessary knowledge, skills, and tools. Many DIY PreAmp Circuit kits and schematics are available online, catering to various skill levels and applications. Building your own PreAmp can be a rewarding experience, allowing you to customize the circuit to your specific requirements and gain a deeper understanding of audio electronics.
Conclusion
PreAmp Circuits are essential components in many audio systems, providing the necessary amplification and signal conditioning to ensure optimal sound quality. By understanding the principles, types, and applications of PreAmp Circuits, you can make informed decisions when designing, selecting, or using them in your audio projects. Whether you are a professional audio engineer, a musician, or an audiophile, a well-designed PreAmp Circuit can significantly enhance your audio experience.
No responses yet