What are PCB CNC Machines?
PCB CNC machines are computer-controlled machines that are specifically designed for the manufacturing of printed circuit boards. These machines use a variety of tools, such as drills, routers, and dispensers, to create the intricate patterns and circuits required for the functioning of electronic devices.
CNC machines work by interpreting computer-aided design (CAD) files and translating them into precise movements of the machine’s tools. This allows for the creation of highly accurate and repeatable PCB designs, even for complex multi-layered boards.
Types of PCB CNC Machines
There are several types of PCB CNC machines, each designed for specific tasks in the PCB manufacturing process:
- Drilling Machines
- Routing Machines
- Solder Paste Dispensing Machines
- Pick and Place Machines
- Optical Inspection Machines
1. Drilling Machines
PCB drilling machines are used to create the holes required for the placement of components and the creation of vias, which are used to connect different layers of the PCB. These machines use high-speed spindles and precision depth control to ensure accurate and clean holes.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| High-speed spindles | Spindle speeds up to 200,000 RPM for clean, precise holes |
| Automatic tool change | Quick and efficient tool changing for multiple drill sizes |
| Depth control | Precise depth control for consistent hole depths |
| Multi-layer capability | Ability to drill through multiple PCB layers simultaneously |
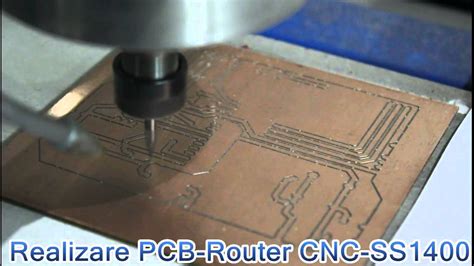
2. Routing Machines
Routing machines are used to cut out the individual PCBs from a larger panel and to create the required shapes and contours. These machines use high-speed spindles and precision XYZ movement to ensure accurate and smooth cuts.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| High-speed spindles | Spindle speeds up to 100,000 RPM for clean, precise cuts |
| Automatic tool change | Quick and efficient tool changing for multiple router bits |
| XYZ movement | Precise XYZ movement for accurate cutting and contouring |
| Vacuum table | Holds the PCB panel securely in place during the routing process |
3. Solder Paste Dispensing Machines
Solder paste dispensing machines are used to apply solder paste to the PCB pads prior to component placement. These machines use precision dispensing heads and computer-controlled movement to ensure accurate and consistent solder paste application.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Precision dispensing | Accurate and consistent solder paste application |
| Computer-controlled | Precise movement for optimal solder paste placement |
| Multiple head options | Ability to use different dispensing heads for various applications |
| Vision systems | Integrated vision systems for automatic alignment and inspection |
4. Pick and Place Machines
Pick and place machines are used to automatically place electronic components onto the PCB. These machines use precision robotics and computer vision systems to ensure accurate and fast component placement.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| High-speed placement | Placement speeds up to 100,000 components per hour |
| Precision robotics | Accurate and repeatable component placement |
| Computer vision | Automatic component alignment and inspection |
| Multiple head options | Ability to use different placement heads for various component types |
5. Optical Inspection Machines
Optical inspection machines are used to automatically inspect the PCBs for defects and errors. These machines use high-resolution cameras and advanced image processing algorithms to detect issues such as missing components, solder bridges, and incorrect component placement.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| High-resolution cameras | Detailed images for accurate defect detection |
| Advanced algorithms | Sophisticated image processing for reliable error detection |
| Multiple lighting options | Different lighting configurations for optimal defect visibility |
| Automatic reporting | Generates detailed inspection reports for quality control |
Benefits of PCB CNC Machines
The use of PCB CNC machines offers several significant benefits over traditional manual PCB manufacturing methods:
- Increased Precision
- Improved Efficiency
- Enhanced Flexibility
- Reduced Labor Costs
- Consistent Quality
1. Increased Precision
PCB CNC machines offer unparalleled precision, with the ability to create intricate designs and fine details that would be impossible to achieve with manual methods. This high level of precision is essential for the manufacturing of high-density, multi-layered PCBs used in advanced electronic devices.
2. Improved Efficiency
CNC machines automate many of the time-consuming tasks involved in PCB manufacturing, such as drilling, routing, and component placement. This automation significantly improves production efficiency, reducing the time required to manufacture PCBs and increasing overall output.
3. Enhanced Flexibility
PCB CNC machines offer greater flexibility in terms of design changes and customization. CAD files can be easily modified and uploaded to the machines, allowing for quick adjustments and prototyping. This flexibility is particularly valuable in the rapidly evolving electronics industry, where product life cycles are short and design changes are frequent.
4. Reduced Labor Costs
The automation provided by PCB CNC machines reduces the need for manual labor, which can significantly lower production costs. This reduction in labor costs allows PCB manufacturers to offer more competitive pricing and invest in further technological advancements.
5. Consistent Quality
CNC machines ensure consistent quality across all manufactured PCBs. By eliminating human error and variability, these machines produce PCBs with uniform characteristics and performance, reducing the likelihood of defects and improving overall product reliability.
Applications of PCB CNC Machines
PCB CNC machines are used in a wide range of industries and applications, including:
- Consumer Electronics
- Automotive Electronics
- Medical Devices
- Aerospace and Defense
- Industrial Control Systems
1. Consumer Electronics
PCB CNC machines are extensively used in the production of consumer electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable devices. The high precision and efficiency offered by these machines are essential for the manufacturing of the compact, high-density PCBs used in these products.
2. Automotive Electronics
The automotive industry relies heavily on PCB CNC machines for the production of various electronic components, such as engine control units, infotainment systems, and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). The reliability and consistent quality provided by these machines are critical for the safety and performance of modern vehicles.
3. Medical Devices
PCB CNC machines are used in the manufacturing of medical devices, such as diagnostic equipment, monitoring systems, and implantable devices. The precision and reliability offered by these machines are essential for the production of PCBs that meet the stringent quality and safety requirements of the medical industry.
4. Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace and defense industries use PCB CNC machines for the production of high-reliability PCBs used in aircraft, satellites, and military equipment. These machines offer the precision and consistency required for the manufacturing of PCBs that can withstand extreme conditions and ensure the proper functioning of critical systems.
5. Industrial Control Systems
PCB CNC machines are used in the production of industrial control systems, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. The reliability and flexibility provided by these machines are essential for the manufacturing of PCBs that can handle the demands of industrial environments.

The Future of PCB CNC Machines
As the electronics industry continues to evolve, the demand for more advanced and efficient PCB manufacturing methods will only increase. The future of PCB CNC machines is likely to be shaped by several key trends and developments:
- Increased Automation
- Adoption of Industry 4.0 Technologies
- Development of New Materials
- Miniaturization and High-Density PCBs
- Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
1. Increased Automation
The trend towards increased automation in PCB manufacturing is expected to continue, with the development of more sophisticated CNC machines that can handle a wider range of tasks with minimal human intervention. This will lead to further improvements in efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness.
2. Adoption of Industry 4.0 Technologies
The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning, into PCB CNC machines will enable more intelligent and adaptive manufacturing processes. These technologies will allow for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and autonomous decision-making, further enhancing the efficiency and reliability of PCB production.
3. Development of New Materials
The development of new materials, such as advanced ceramics, high-performance polymers, and nanomaterials, will drive the need for PCB CNC machines that can handle these materials effectively. These machines will need to be equipped with specialized tools and processing capabilities to accommodate the unique properties and requirements of these new materials.
4. Miniaturization and High-Density PCBs
As electronic devices continue to become smaller and more powerful, the demand for miniaturized and high-density PCBs will increase. PCB CNC machines will need to evolve to meet the challenges of manufacturing these complex boards, with higher precision, finer feature sizes, and the ability to handle more layers and smaller components.
5. Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
The growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility will drive the development of PCB CNC machines that are more energy-efficient, generate less waste, and use eco-friendly materials. Manufacturers will need to adopt sustainable practices and technologies to meet the increasing demand for greener electronics and comply with stricter environmental regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the difference between a PCB CNC machine and a traditional CNC machine?
-
A PCB CNC machine is specifically designed for the manufacturing of printed circuit boards, while traditional CNC machines are used for a wider range of applications, such as machining metal parts. PCB CNC machines are equipped with specialized tools and features, such as high-speed spindles, automatic tool changers, and vision systems, that are optimized for PCB production.
-
How accurate are PCB CNC machines?
-
PCB CNC machines offer high levels of accuracy, with modern machines capable of achieving positioning accuracies of ±0.01 mm or better. This level of precision is essential for the manufacturing of high-density, multi-layered PCBs used in advanced electronic devices.
-
What is the typical lifespan of a PCB CNC machine?
-
The lifespan of a PCB CNC machine can vary depending on factors such as usage, maintenance, and the specific model. However, with proper care and maintenance, a high-quality PCB CNC machine can last for 10-15 years or more.
-
How long does it take to set up a new PCB design on a CNC machine?
-
The setup time for a new PCB design on a CNC machine can vary depending on the complexity of the design and the specific machine being used. However, with modern CAD/CAM software and automated setup features, the setup process can often be completed in a matter of minutes.
-
Can PCB CNC machines handle both prototype and high-volume production?
- Yes, PCB CNC machines are versatile and can be used for both prototype and high-volume production. The flexibility and quick setup times of these machines make them ideal for prototyping and small-batch production, while their speed and efficiency enable them to handle larger production runs as well.
Conclusion
PCB CNC machines have revolutionized the electronics manufacturing industry, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and flexibility in the production of printed circuit boards. These high-tech machines have become essential tools for businesses across a wide range of industries, from consumer electronics and automotive to medical devices and aerospace.
As the demand for more advanced and miniaturized electronic devices continues to grow, the role of PCB CNC machines will only become more critical. The future of these machines lies in increased automation, the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, the development of new materials, and a focus on sustainable manufacturing practices.
By embracing these advancements and investing in the latest PCB CNC technology, manufacturers can position themselves to meet the evolving needs of the electronics industry and deliver innovative, high-quality products to their customers.
No responses yet